5 Costly ‘ERP vs CRM’ Confusions Impacting Your Bottom Line
Why do many businesses need help differentiating between ERP and CRM software despite their crucial roles in driving organizational success?
Companies require more than just intuitive decision-making to stay ahead of the competition. It demands efficient management of resources, streamlined processes, and nurturing lasting relationships with customers.
To achieve these objectives, many organizations turn to specialized software solutions. Two such prominent tools are Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems.
While both aim to enhance organizational efficiency, they serve distinct purposes and cater to different aspects of business operations.
In this comprehensive blog, we delve into the nuances of ERP and CRM software, unraveling their functionalities, strengths, and application areas.
Whether you’re a small startup or a multinational corporation, understanding the disparities between these systems is crucial for making informed decisions about which aligns best with your business needs.
Challenges and opportunities for SMBs
| Challenges | Opportunities |
| Limited resources Operational Issues Low on Funds if bootstrapped Limited IT infrastructure Limited team members Scalability is yet another significant issue for SMBs. Changing growth requirements | Technology can enhance- productivity, efficiency, and Improve sales and profitability Automation of sales Simplify operations Time Management Finance Management Personalized service Rapid response times, and Strong customer, vendor, and employee relationships |
What is an ERP System?
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning, which refers to a type of software businesses use to handle day-to-day operations and business activities such as procurement, project and risk management, and accounting.
An Enterprise Resource Planning software system coordinates organizes, and integrates corporate processes in a centralized location.
An ERP system optimizes and integrates various business processes across different organizational departments. It typically includes finance, human resources, inventory management, supply chain management, and production planning modules.
By integrating these core business processes, an ERP system improves efficiency, reduces operational costs, and enhances decision-making capabilities.
An ERP system helps businesses eliminate costs, minimize errors, and improve overall productivity through automation and standardization of processes.
The ultimate objective of an ERP system is to reduce costs, increase operational efficiency, and enable better resource allocation and strategic decision-making.


What is a CRM System?
Customer relationship management, also known as CRM, is software that helps sales teams and companies organize their interactions with prospects and customers and provides visibility across the organization to better support a company’s goals.
A CRM system manages interactions and relationships with current and potential customers. It helps businesses track customer interactions, manage leads, and streamline sales processes.
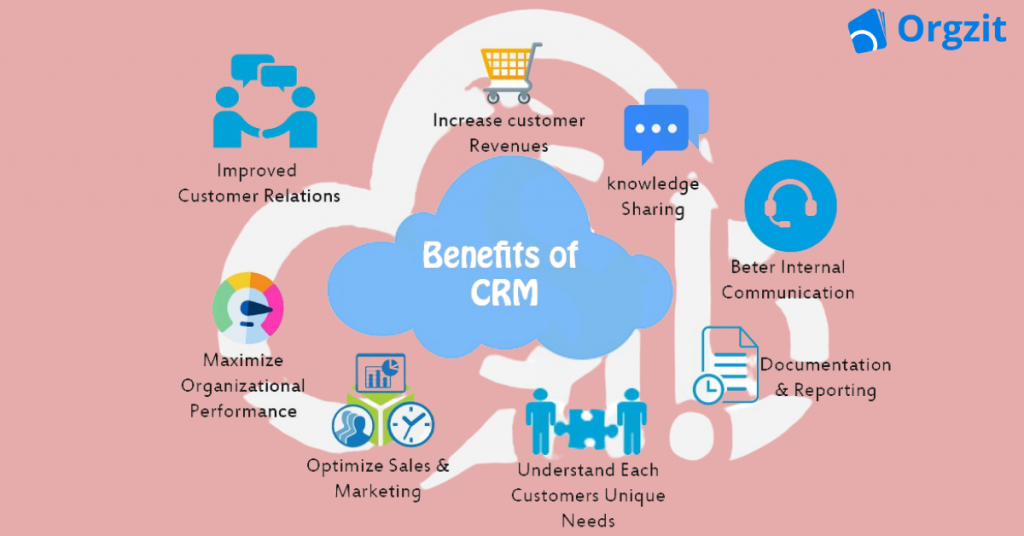
A CRM system helps improve sales and revenue generation by effectively managing customer relationships. It enables businesses to identify potential sales opportunities, nurture leads, and provide personalized experiences to customers.
Ultimately, the primary goal of a CRM system is to increase sales and customer satisfaction, leading to enhanced profitability.

ERP VS CRM: DO YOU NEED ANY ONE OR BOTH?
Similarity
Differences
Benefits
- ERP and CRM are business software applications that utilize relational databases for data storage and analysis.
- Available either on-premises or as software as a service (SaaS), with clients accessing it through the cloud.
- ERP and CRM systems are both essential for organizations, but;
- ERP is primarily used for reducing costs.
- CRM is used for customer data by sales and customer care departments, referred to as the front office.
- CRM and ERP systems are tools for businesses to manage customer data and make informed decisions.
- CRM provides a central repository for customer data, enabling sales reps to respond to outstanding customer service tickets and identify high-value customers.
- ERP systems offer a single, shared database for financial and operational data, enabling faster decisions and reduced close times.
5 ways in which a wrong software solution can impact your business goals
- Inefficient Resource Allocation: Confusion between ERP and CRM systems can lead to misallocation of resources, such as workforce and financial investments. For example, if a business invests in CRM functionalities expecting comprehensive resource planning features, it may miss out on crucial ERP capabilities, resulting in inefficiencies and wasted resources.
- Lost Productivity: Misunderstanding the differences between ERP and CRM software can confuse employees regarding which system to use for specific tasks. This confusion can lead to decreased productivity as employees waste time navigating between systems or attempting to use one system for functions it’s not designed for, ultimately impacting the overall output of the business.
- Duplication of Efforts: Without clear distinctions between ERP and CRM functionalities, businesses may inadvertently duplicate efforts by entering the same data into both systems. This duplication wastes time and increases the likelihood of errors and inconsistencies in data, leading to inaccurate reporting and decision-making.
- Missed Opportunities for Customer Engagement: CRM systems are essential for managing customer relationships and improving customer satisfaction. However, suppose a business mistakenly focuses solely on ERP functionalities and neglects CRM capabilities. In that case, it may miss out on valuable opportunities to engage with customers, leading to decreased customer loyalty and potential revenue loss.
- Ineffective Decision-Making: ERP and CRM systems provide valuable insights into different aspects of business operations and customer interactions. Confusion between the two can result in incomplete or inaccurate data analysis, leading to poor decision-making by business leaders. Without access to comprehensive and accurate information from both systems, businesses may struggle to identify trends, forecast future needs, and make strategic decisions, ultimately impacting their bottom line.


Advantages of cloud-based ERP and CRM for SMBs:
- Cutting edge over other small and medium-sized businesses: When an SMB employs cloud apps for key business functions, its teams may focus more on growth objectives. This provides a competitive advantage while competing against other SMBs in their industry.
- A competitive equalizer with major corporations: Often, an SMB will be pursuing market share or concepts held by larger organizations, many of whom are already modernizing their enterprises through the use of cloud applications.
Instead of constructing their own IT stack, larger firms save money on IT infrastructure and make their operations more efficient, flexible, and safe. By adopting a cloud-first strategy, SMBs may use the same software and infrastructure as their larger rivals today. And if those larger firms have not yet adopted cloud apps, an SMB still obtains another competitive edge.
Winding Up
Common Goals
While CRM and ERP systems serve different functions within an organization, they both aim to increase the company’s operational and financial efficiency.
CRM systems improve profitability by improving sales, increasing customer retention, and fostering long-term customer relationships.
ERP systems contribute to profitability by optimizing business processes, reducing costs, enhancing productivity, and enabling better resource management.
Together, CRM and ERP systems provide a comprehensive solution for businesses to maximize growth, enhance efficiency, and drive profitability in a competitive market environment.
To conclude, we can deduce that companies need both a CRM and an ERP system to maximize business growth. One improves sales, and those revenues facilitate business processes. Then, an ERP system optimizes those business processes.
FAQs
Enterprise Resource Planning refers to a type of software businesses use to handle day-to-day operations and business activities such as procurement, project and risk management, and accounting.
Customer relationship management, or CRM, is software that helps sales teams and companies organize their interactions with prospects and customers. It provides visibility across the organization to support better a company’s goals.
While ERP and CRM have many similarities and common benefits, they are not interchangeable.
If you are a sales-driven company, your core software should be CRM. And if you aim to address operational inefficiencies or reduce overall costs, your core software should be ERP. ERP is best suited for manufacturing companies.
Yes, absolutely. Most of the ERP and CRM software available today can be integrated together.
Thank you for reading our blog!
Struggling to find the right software solution for your business? Get a Free Consultation from our SOFTWARE SOLUTION EXPERT Now!











